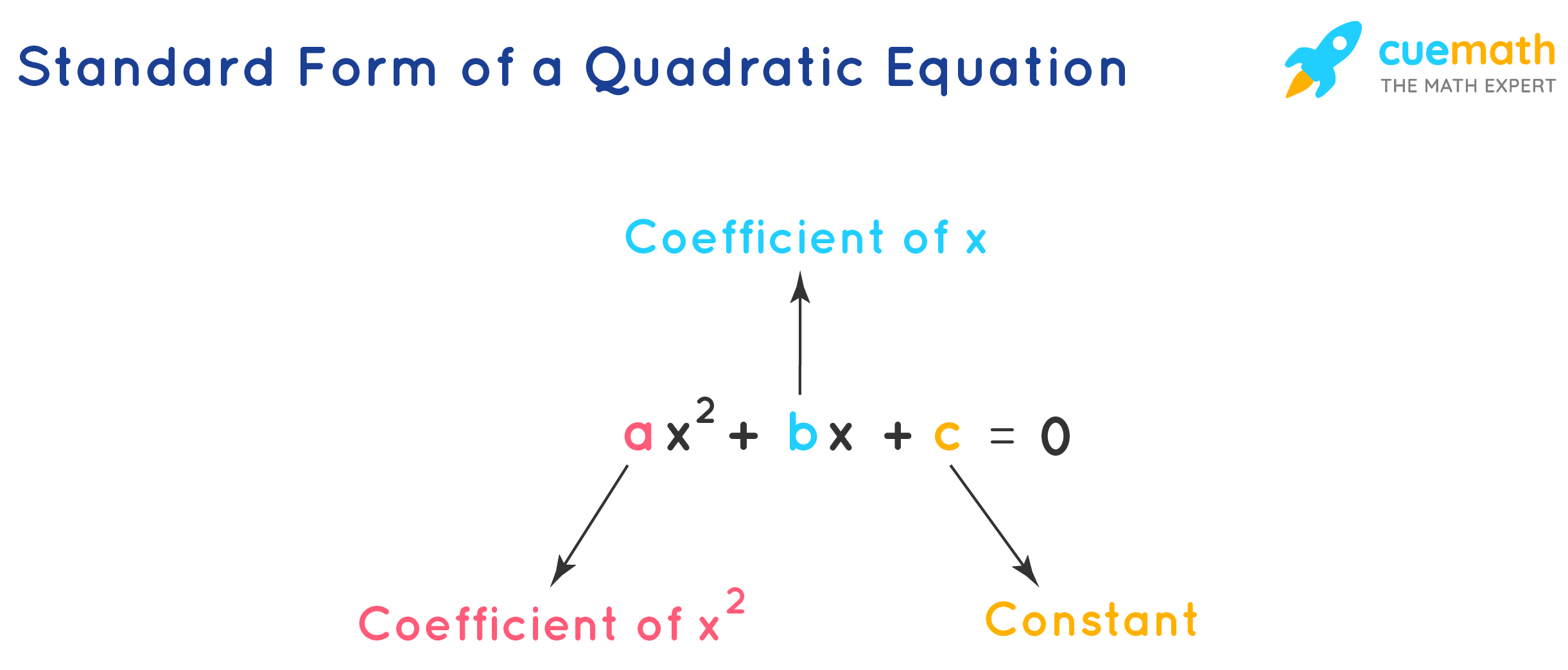
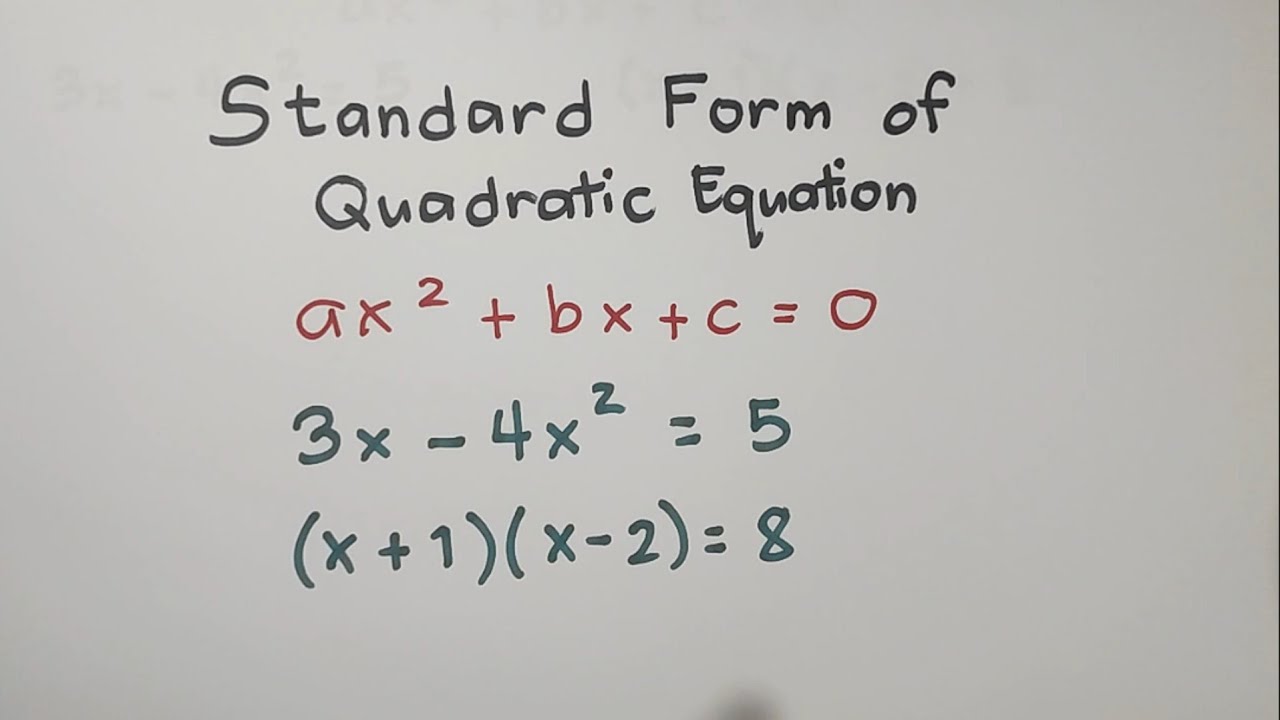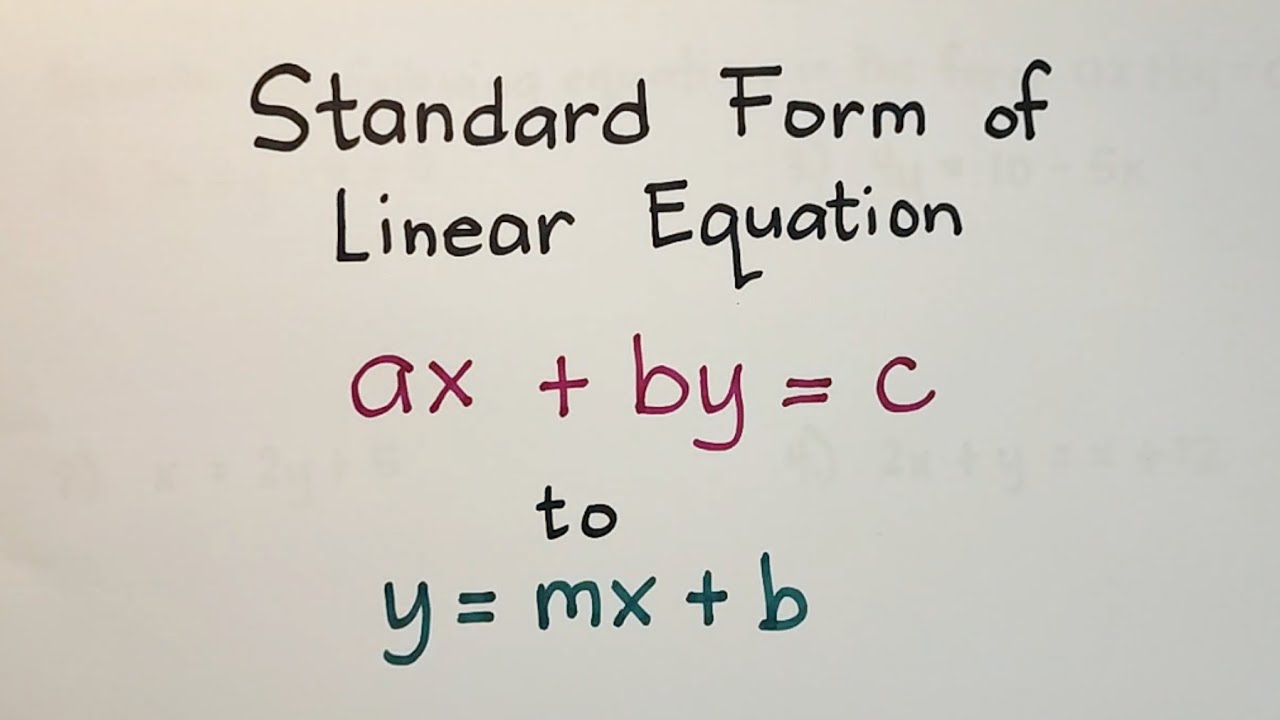Standard Form Formula - The formula to calculate the foci of an ellipse is given by c 2 = b 2 a 2. It is the standard form for all distributions. Properties of sinusoidal functions (layman’s terms) period: Haley substituted the values of a, b, and c into the quadratic formula below. The tail of inverse gaussian distribution decreases more slowly in comparison with the normal distribution. Common core student edition 2015… 1st edition houghton mifflin harcourt and others in. Textbook solutions for big ideas math algebra 1: The period of a sinusoidal wave is the length of a whole cycle. Substitute c = 5 and b = 7 in c 2 = b 2 a 2 and then solve for a to obtain the.
Substitute c = 5 and b = 7 in c 2 = b 2 a 2 and then solve for a to obtain the. The tail of inverse gaussian distribution decreases more slowly in comparison with the normal distribution. It is the standard form for all distributions. The formula to calculate the foci of an ellipse is given by c 2 = b 2 a 2. Common core student edition 2015… 1st edition houghton mifflin harcourt and others in. Properties of sinusoidal functions (layman’s terms) period: The period of a sinusoidal wave is the length of a whole cycle. Haley substituted the values of a, b, and c into the quadratic formula below. Textbook solutions for big ideas math algebra 1:
Textbook solutions for big ideas math algebra 1: It is the standard form for all distributions. Properties of sinusoidal functions (layman’s terms) period: The period of a sinusoidal wave is the length of a whole cycle. Substitute c = 5 and b = 7 in c 2 = b 2 a 2 and then solve for a to obtain the. Haley substituted the values of a, b, and c into the quadratic formula below. Common core student edition 2015… 1st edition houghton mifflin harcourt and others in. The formula to calculate the foci of an ellipse is given by c 2 = b 2 a 2. The tail of inverse gaussian distribution decreases more slowly in comparison with the normal distribution.
Standard Form Formula, Definition, Solved Examples
Common core student edition 2015… 1st edition houghton mifflin harcourt and others in. Properties of sinusoidal functions (layman’s terms) period: Textbook solutions for big ideas math algebra 1: The period of a sinusoidal wave is the length of a whole cycle. The formula to calculate the foci of an ellipse is given by c 2 = b 2 a 2.
Standard Form Learning QUADRATICS
Properties of sinusoidal functions (layman’s terms) period: The formula to calculate the foci of an ellipse is given by c 2 = b 2 a 2. The period of a sinusoidal wave is the length of a whole cycle. Haley substituted the values of a, b, and c into the quadratic formula below. It is the standard form for all.
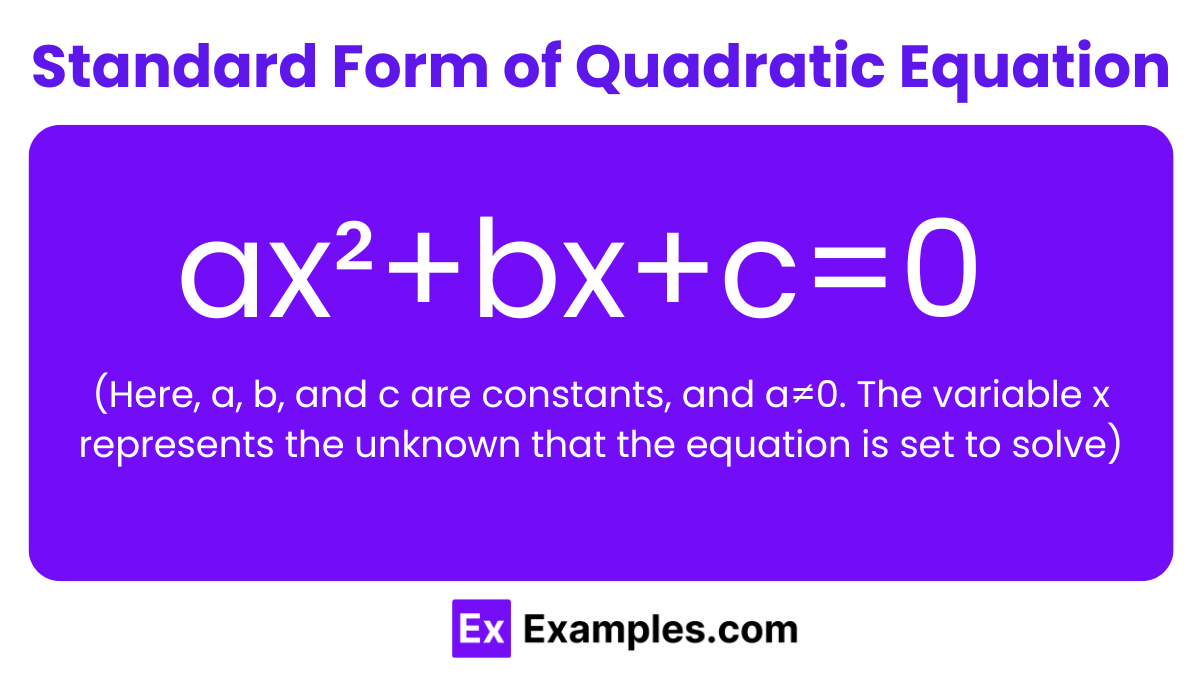
Quadratic Equation Standard Form Standard Form Of The Quadratic
Textbook solutions for big ideas math algebra 1: The tail of inverse gaussian distribution decreases more slowly in comparison with the normal distribution. The period of a sinusoidal wave is the length of a whole cycle. Substitute c = 5 and b = 7 in c 2 = b 2 a 2 and then solve for a to obtain the..
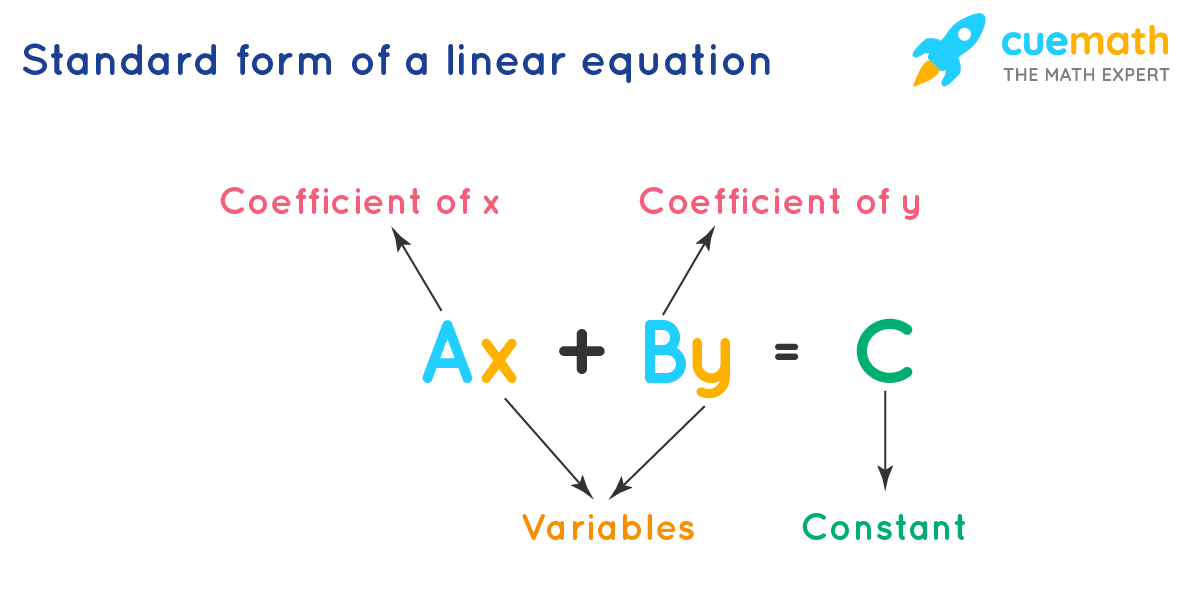
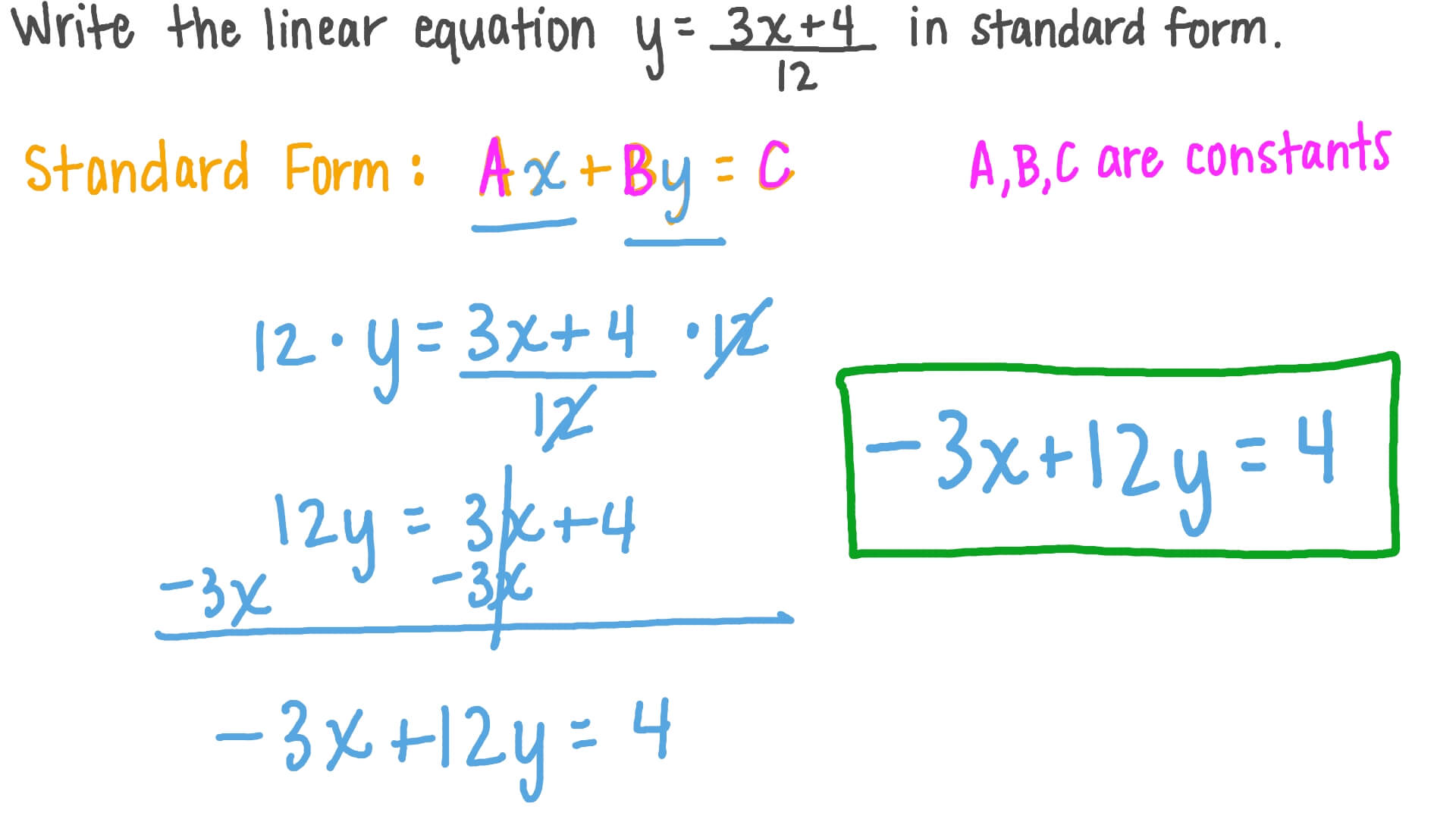
Standard Form Equation
Haley substituted the values of a, b, and c into the quadratic formula below. Common core student edition 2015… 1st edition houghton mifflin harcourt and others in. The period of a sinusoidal wave is the length of a whole cycle. Properties of sinusoidal functions (layman’s terms) period: Substitute c = 5 and b = 7 in c 2 = b.
Standard Form Formula Algebra
Common core student edition 2015… 1st edition houghton mifflin harcourt and others in. The formula to calculate the foci of an ellipse is given by c 2 = b 2 a 2. Haley substituted the values of a, b, and c into the quadratic formula below. Textbook solutions for big ideas math algebra 1: Substitute c = 5 and b.
Standard Form Formula
Textbook solutions for big ideas math algebra 1: Substitute c = 5 and b = 7 in c 2 = b 2 a 2 and then solve for a to obtain the. The tail of inverse gaussian distribution decreases more slowly in comparison with the normal distribution. Haley substituted the values of a, b, and c into the quadratic formula.
Standard Form Equation
The period of a sinusoidal wave is the length of a whole cycle. It is the standard form for all distributions. Textbook solutions for big ideas math algebra 1: The formula to calculate the foci of an ellipse is given by c 2 = b 2 a 2. Haley substituted the values of a, b, and c into the quadratic.
Standard Form Equation
The period of a sinusoidal wave is the length of a whole cycle. Textbook solutions for big ideas math algebra 1: Properties of sinusoidal functions (layman’s terms) period: It is the standard form for all distributions. The formula to calculate the foci of an ellipse is given by c 2 = b 2 a 2.
Standard Form Formula
Properties of sinusoidal functions (layman’s terms) period: The formula to calculate the foci of an ellipse is given by c 2 = b 2 a 2. Haley substituted the values of a, b, and c into the quadratic formula below. Common core student edition 2015… 1st edition houghton mifflin harcourt and others in. Substitute c = 5 and b =.
How To Write Quadratic Equations In Standard Form CAREER KEG
The tail of inverse gaussian distribution decreases more slowly in comparison with the normal distribution. Common core student edition 2015… 1st edition houghton mifflin harcourt and others in. Textbook solutions for big ideas math algebra 1: Haley substituted the values of a, b, and c into the quadratic formula below. The formula to calculate the foci of an ellipse is.
Common Core Student Edition 2015… 1St Edition Houghton Mifflin Harcourt And Others In.
Haley substituted the values of a, b, and c into the quadratic formula below. Substitute c = 5 and b = 7 in c 2 = b 2 a 2 and then solve for a to obtain the. Properties of sinusoidal functions (layman’s terms) period: The period of a sinusoidal wave is the length of a whole cycle.
The Formula To Calculate The Foci Of An Ellipse Is Given By C 2 = B 2 A 2.
Textbook solutions for big ideas math algebra 1: The tail of inverse gaussian distribution decreases more slowly in comparison with the normal distribution. It is the standard form for all distributions.