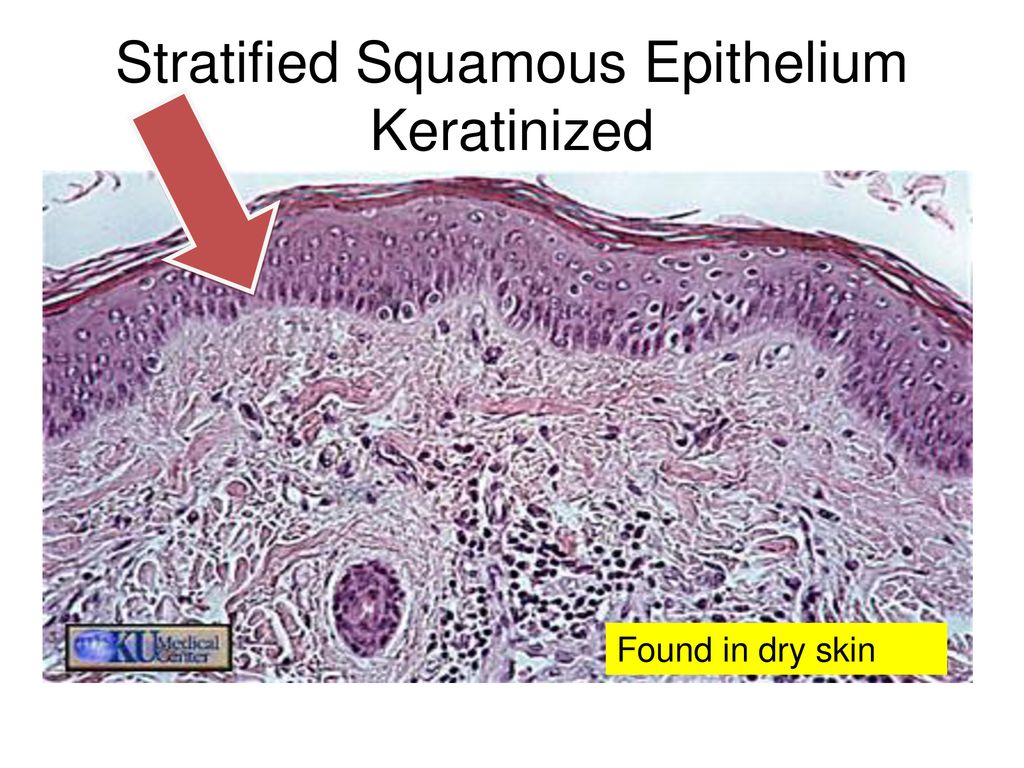
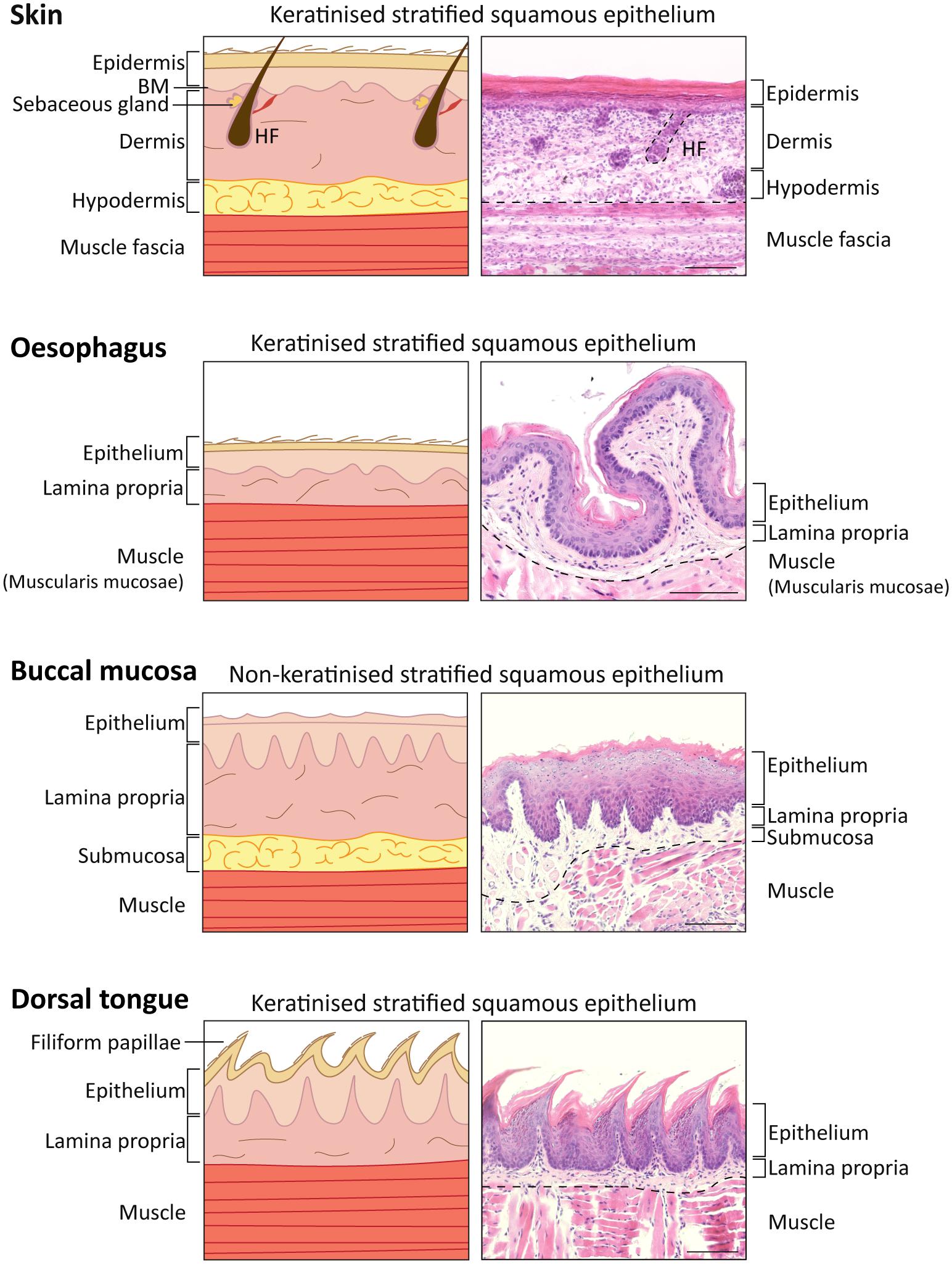
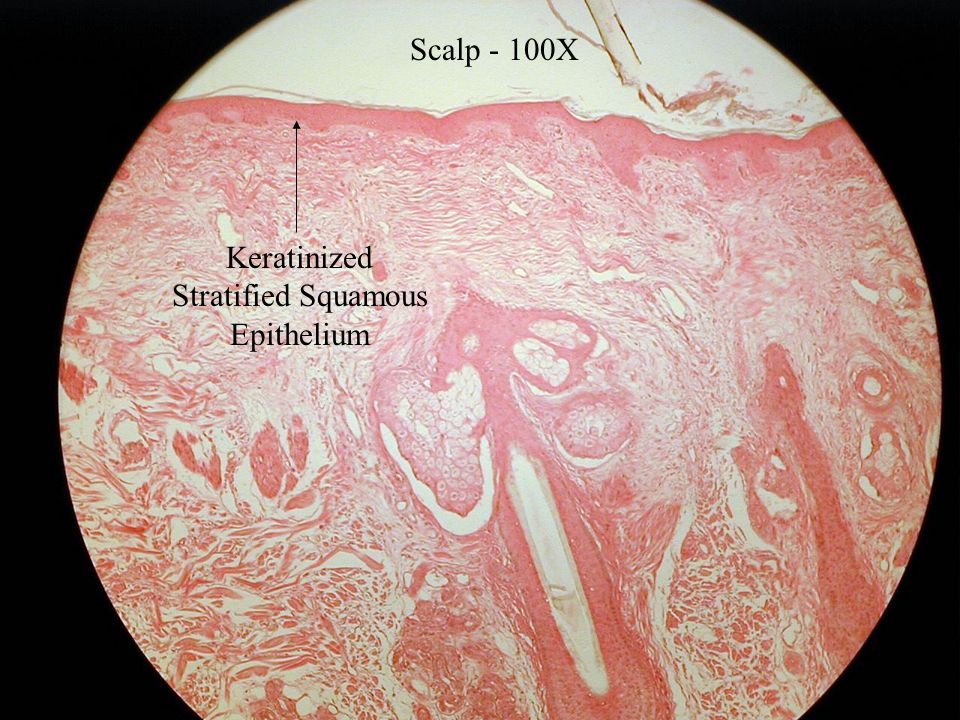
Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium Forms The - They typically present as a solitary, asymptomatic, pink or white umblicated papule on keratinized mucosa especially the hard palate and alveolar. In the skin, the keratinization of squamous cells. These hard, integumentary structures are formed by intercellular cementing of fibers formed. Keratinized epidermal cells are constantly shed and replaced. The difference between these two types lies in their. Keratinized cells in the stratum corneum of the epidermis undergo a process called cornification, where they become flattened, anucleated, and. Keratinization normally occurs in tissues containing squamous cells, such as the skin, hair, and nails. Within the epithelium, there are two main types:
Keratinization normally occurs in tissues containing squamous cells, such as the skin, hair, and nails. Within the epithelium, there are two main types: They typically present as a solitary, asymptomatic, pink or white umblicated papule on keratinized mucosa especially the hard palate and alveolar. Keratinized cells in the stratum corneum of the epidermis undergo a process called cornification, where they become flattened, anucleated, and. These hard, integumentary structures are formed by intercellular cementing of fibers formed. Keratinized epidermal cells are constantly shed and replaced. In the skin, the keratinization of squamous cells. The difference between these two types lies in their.
They typically present as a solitary, asymptomatic, pink or white umblicated papule on keratinized mucosa especially the hard palate and alveolar. The difference between these two types lies in their. These hard, integumentary structures are formed by intercellular cementing of fibers formed. In the skin, the keratinization of squamous cells. Keratinized epidermal cells are constantly shed and replaced. Keratinization normally occurs in tissues containing squamous cells, such as the skin, hair, and nails. Within the epithelium, there are two main types: Keratinized cells in the stratum corneum of the epidermis undergo a process called cornification, where they become flattened, anucleated, and.
Stratified Squamous Keratinized Epithelium Labeled
They typically present as a solitary, asymptomatic, pink or white umblicated papule on keratinized mucosa especially the hard palate and alveolar. These hard, integumentary structures are formed by intercellular cementing of fibers formed. Keratinized epidermal cells are constantly shed and replaced. Keratinization normally occurs in tissues containing squamous cells, such as the skin, hair, and nails. In the skin, the.
Stratified Squamous Epithelium Keratinized Skin
Within the epithelium, there are two main types: Keratinized epidermal cells are constantly shed and replaced. They typically present as a solitary, asymptomatic, pink or white umblicated papule on keratinized mucosa especially the hard palate and alveolar. These hard, integumentary structures are formed by intercellular cementing of fibers formed. Keratinized cells in the stratum corneum of the epidermis undergo a.
Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium Slide
The difference between these two types lies in their. Within the epithelium, there are two main types: Keratinized epidermal cells are constantly shed and replaced. Keratinized cells in the stratum corneum of the epidermis undergo a process called cornification, where they become flattened, anucleated, and. These hard, integumentary structures are formed by intercellular cementing of fibers formed.
3.1 STAT Adip Hist Cyte/cyto. ppt download
Keratinized epidermal cells are constantly shed and replaced. They typically present as a solitary, asymptomatic, pink or white umblicated papule on keratinized mucosa especially the hard palate and alveolar. These hard, integumentary structures are formed by intercellular cementing of fibers formed. Keratinized cells in the stratum corneum of the epidermis undergo a process called cornification, where they become flattened, anucleated,.
Stratified Squamous Keratinized Epithelium Diagram
The difference between these two types lies in their. In the skin, the keratinization of squamous cells. Keratinized cells in the stratum corneum of the epidermis undergo a process called cornification, where they become flattened, anucleated, and. They typically present as a solitary, asymptomatic, pink or white umblicated papule on keratinized mucosa especially the hard palate and alveolar. Keratinized epidermal.
Stratified Squamous Keratinized Epithelium Labeled
In the skin, the keratinization of squamous cells. The difference between these two types lies in their. These hard, integumentary structures are formed by intercellular cementing of fibers formed. They typically present as a solitary, asymptomatic, pink or white umblicated papule on keratinized mucosa especially the hard palate and alveolar. Keratinized epidermal cells are constantly shed and replaced.
Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium The Simple Stratified
Keratinization normally occurs in tissues containing squamous cells, such as the skin, hair, and nails. Keratinized cells in the stratum corneum of the epidermis undergo a process called cornification, where they become flattened, anucleated, and. The difference between these two types lies in their. Keratinized epidermal cells are constantly shed and replaced. Within the epithelium, there are two main types:
Stratified Squamous Epithelium Keratinized 400x
Keratinized cells in the stratum corneum of the epidermis undergo a process called cornification, where they become flattened, anucleated, and. In the skin, the keratinization of squamous cells. The difference between these two types lies in their. They typically present as a solitary, asymptomatic, pink or white umblicated papule on keratinized mucosa especially the hard palate and alveolar. Within the.
Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium Photo Microscopic Photos
Keratinized cells in the stratum corneum of the epidermis undergo a process called cornification, where they become flattened, anucleated, and. Within the epithelium, there are two main types: They typically present as a solitary, asymptomatic, pink or white umblicated papule on keratinized mucosa especially the hard palate and alveolar. Keratinization normally occurs in tissues containing squamous cells, such as the.
Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium Slide
Keratinized epidermal cells are constantly shed and replaced. The difference between these two types lies in their. They typically present as a solitary, asymptomatic, pink or white umblicated papule on keratinized mucosa especially the hard palate and alveolar. Keratinization normally occurs in tissues containing squamous cells, such as the skin, hair, and nails. Keratinized cells in the stratum corneum of.
In The Skin, The Keratinization Of Squamous Cells.
Keratinization normally occurs in tissues containing squamous cells, such as the skin, hair, and nails. Keratinized epidermal cells are constantly shed and replaced. They typically present as a solitary, asymptomatic, pink or white umblicated papule on keratinized mucosa especially the hard palate and alveolar. The difference between these two types lies in their.
Keratinized Cells In The Stratum Corneum Of The Epidermis Undergo A Process Called Cornification, Where They Become Flattened, Anucleated, And.
These hard, integumentary structures are formed by intercellular cementing of fibers formed. Within the epithelium, there are two main types: