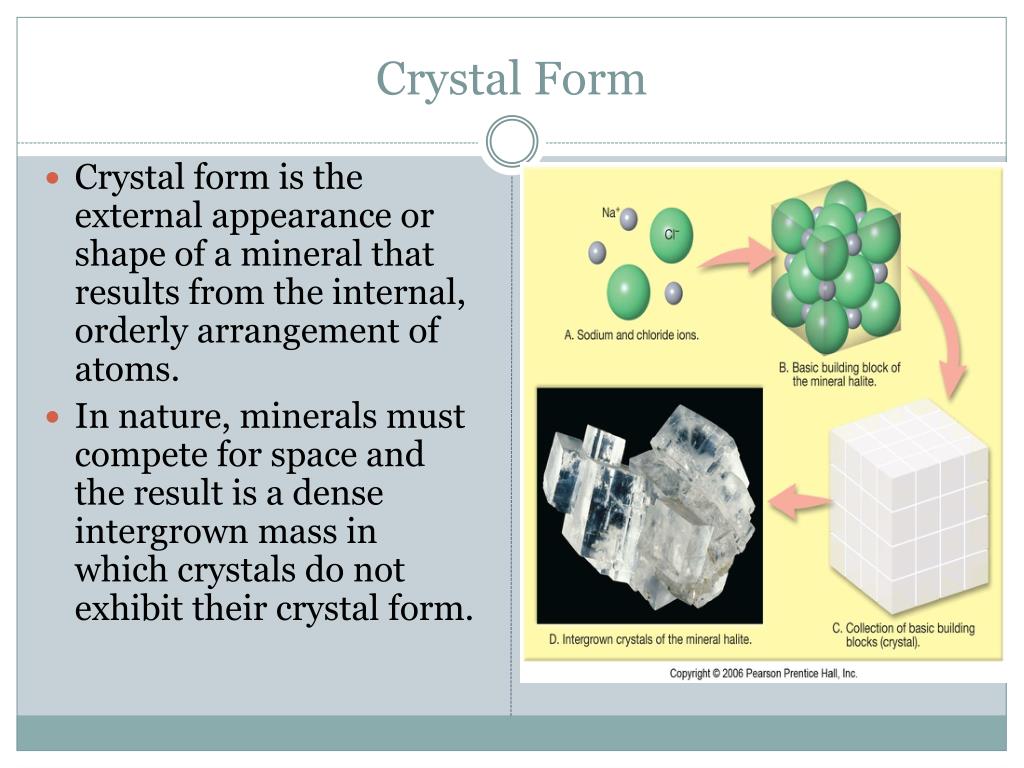
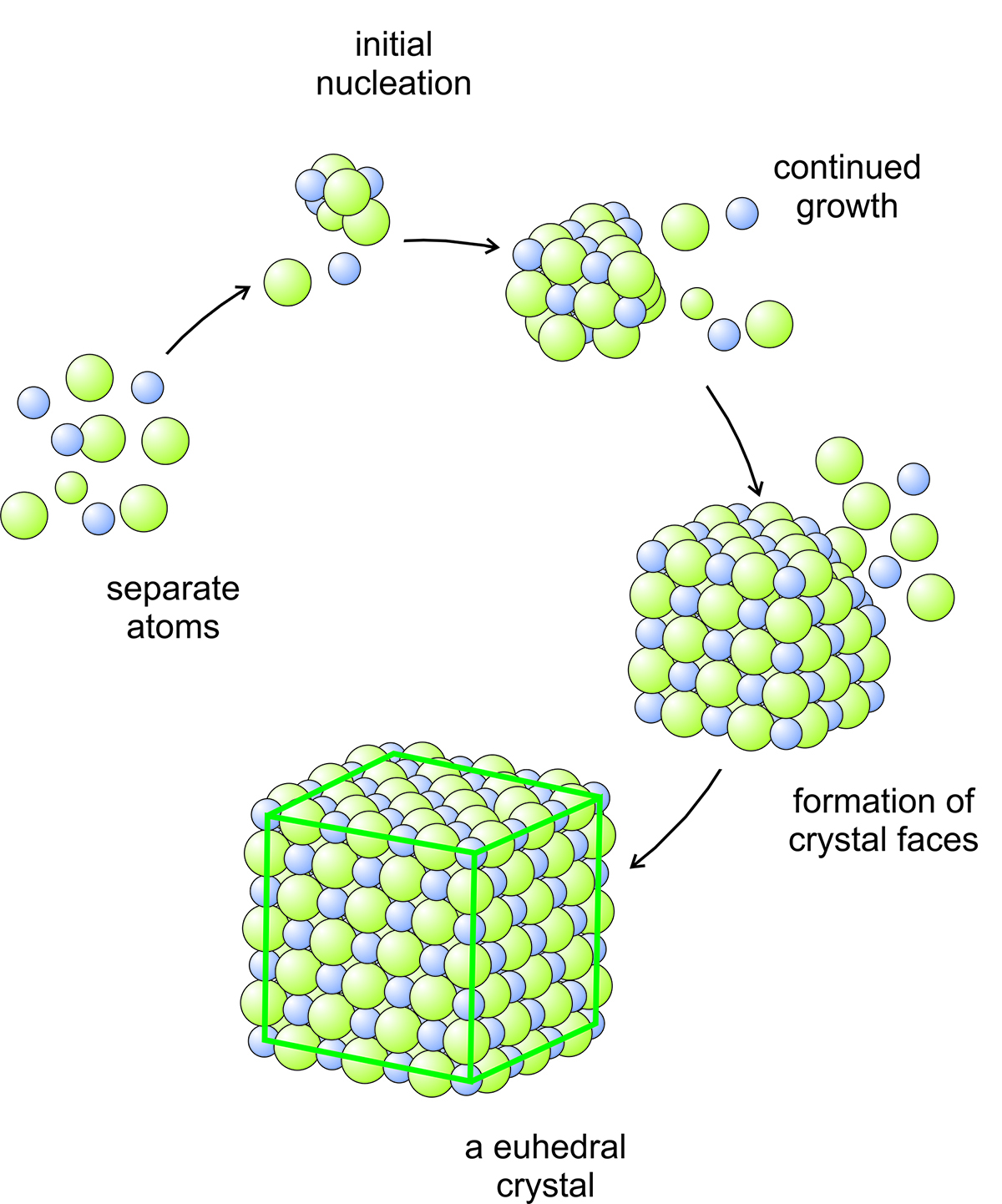
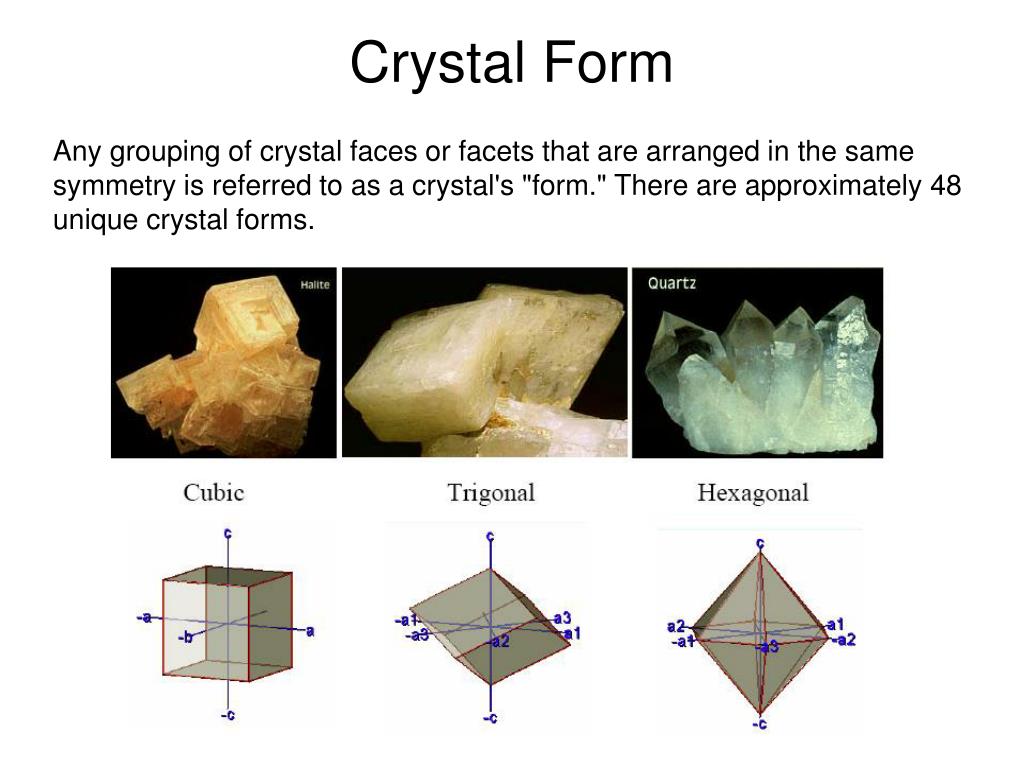
How Do Crystals Form - How do crystals form & grow? Crystals may be classified by their bonding type (e.g., ionic, covalent) or their lattice structure (e.g., cubic, hexagonal). A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents, such as atoms, molecules or ions,. Not all crystals form in water, but nearly all crystals form the same way, atoms come together and become a uniformed cluster. The crystallization process begins with nucleation, the initial step where a small number of particles (that is, ions, atoms, or molecules) come together.
Crystals may be classified by their bonding type (e.g., ionic, covalent) or their lattice structure (e.g., cubic, hexagonal). Not all crystals form in water, but nearly all crystals form the same way, atoms come together and become a uniformed cluster. How do crystals form & grow? The crystallization process begins with nucleation, the initial step where a small number of particles (that is, ions, atoms, or molecules) come together. A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents, such as atoms, molecules or ions,.
Crystals may be classified by their bonding type (e.g., ionic, covalent) or their lattice structure (e.g., cubic, hexagonal). How do crystals form & grow? Not all crystals form in water, but nearly all crystals form the same way, atoms come together and become a uniformed cluster. A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents, such as atoms, molecules or ions,. The crystallization process begins with nucleation, the initial step where a small number of particles (that is, ions, atoms, or molecules) come together.
PPT Physical Properties of Minerals PowerPoint Presentation, free
The crystallization process begins with nucleation, the initial step where a small number of particles (that is, ions, atoms, or molecules) come together. Crystals may be classified by their bonding type (e.g., ionic, covalent) or their lattice structure (e.g., cubic, hexagonal). How do crystals form & grow? Not all crystals form in water, but nearly all crystals form the same.
Crystal Lattice — Structure & Formation Expii
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents, such as atoms, molecules or ions,. Not all crystals form in water, but nearly all crystals form the same way, atoms come together and become a uniformed cluster. The crystallization process begins with nucleation, the initial step where a small number of particles (that is, ions, atoms, or molecules).
Mineral Occurrence, Formation, Compound Britannica
Crystals may be classified by their bonding type (e.g., ionic, covalent) or their lattice structure (e.g., cubic, hexagonal). The crystallization process begins with nucleation, the initial step where a small number of particles (that is, ions, atoms, or molecules) come together. How do crystals form & grow? Not all crystals form in water, but nearly all crystals form the same.
How to Grow Crystals Science Notes and Projects
The crystallization process begins with nucleation, the initial step where a small number of particles (that is, ions, atoms, or molecules) come together. How do crystals form & grow? A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents, such as atoms, molecules or ions,. Crystals may be classified by their bonding type (e.g., ionic, covalent) or their lattice.
What is a Crystal? Let's Talk Science
Crystals may be classified by their bonding type (e.g., ionic, covalent) or their lattice structure (e.g., cubic, hexagonal). The crystallization process begins with nucleation, the initial step where a small number of particles (that is, ions, atoms, or molecules) come together. A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents, such as atoms, molecules or ions,. How do.
4 Crystals and Crystallization Mineralogy
Not all crystals form in water, but nearly all crystals form the same way, atoms come together and become a uniformed cluster. The crystallization process begins with nucleation, the initial step where a small number of particles (that is, ions, atoms, or molecules) come together. How do crystals form & grow? Crystals may be classified by their bonding type (e.g.,.
Crystal Shapes & Forms Rock'n Spirit
How do crystals form & grow? Crystals may be classified by their bonding type (e.g., ionic, covalent) or their lattice structure (e.g., cubic, hexagonal). The crystallization process begins with nucleation, the initial step where a small number of particles (that is, ions, atoms, or molecules) come together. Not all crystals form in water, but nearly all crystals form the same.
Mineral Occurrence, Formation, Compound Britannica
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents, such as atoms, molecules or ions,. The crystallization process begins with nucleation, the initial step where a small number of particles (that is, ions, atoms, or molecules) come together. Not all crystals form in water, but nearly all crystals form the same way, atoms come together and become a.
Crystal Structure and Crystal Systems
Not all crystals form in water, but nearly all crystals form the same way, atoms come together and become a uniformed cluster. How do crystals form & grow? Crystals may be classified by their bonding type (e.g., ionic, covalent) or their lattice structure (e.g., cubic, hexagonal). The crystallization process begins with nucleation, the initial step where a small number of.
PPT Lecture 9 Rocks and Minerals PowerPoint Presentation, free
Crystals may be classified by their bonding type (e.g., ionic, covalent) or their lattice structure (e.g., cubic, hexagonal). A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents, such as atoms, molecules or ions,. Not all crystals form in water, but nearly all crystals form the same way, atoms come together and become a uniformed cluster. The crystallization process.
The Crystallization Process Begins With Nucleation, The Initial Step Where A Small Number Of Particles (That Is, Ions, Atoms, Or Molecules) Come Together.
How do crystals form & grow? A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents, such as atoms, molecules or ions,. Crystals may be classified by their bonding type (e.g., ionic, covalent) or their lattice structure (e.g., cubic, hexagonal). Not all crystals form in water, but nearly all crystals form the same way, atoms come together and become a uniformed cluster.